+ve Amplifying Climate Feedbacks
Arctic
climate feedbacks
Methane from of sub sea floor methane hydrates.
The greatest risk from global warming to humanity and all life
is the multiple combined 'cascading' Arctic climate feed backs.
is the multiple combined 'cascading' Arctic climate feed backs.
These are the following.
o Melting back of subarctic spring-summer snow cover.
o Melting decline of Arctic summer sea ice extent.
o Warming far north peat lands - emits methane.
o Thawing permafrost - emitting methane & nitrous oxide.
o Melting sea floor Arctic methane hydrate - methane.
o Melting decline of Arctic summer sea ice extent.
o Warming far north peat lands - emits methane.
o Thawing permafrost - emitting methane & nitrous oxide.
o Melting sea floor Arctic methane hydrate - methane.
Methane and nitrous oxide are much more powerful greenhouse gases than CO2.
Methane from of sub sea floor methane hydrates.
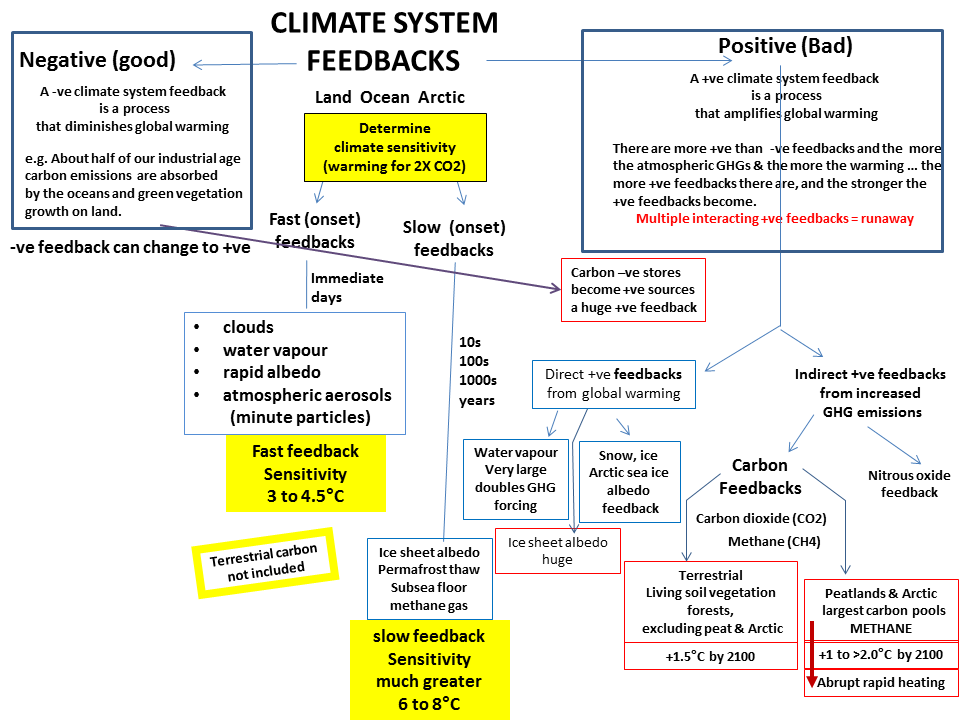
Positive and negative feedback
There are two kinds of feedback in terms of amplifying warming (+ve) or reducing warming (-ve).
We are most used to negative feedback systems used for safety. If a heater gets to hot there is a built -ve feedback that switches it off.
But in the climate system there is no such safety mechanism- feedbacks act in the dangerously +ve feedback way.
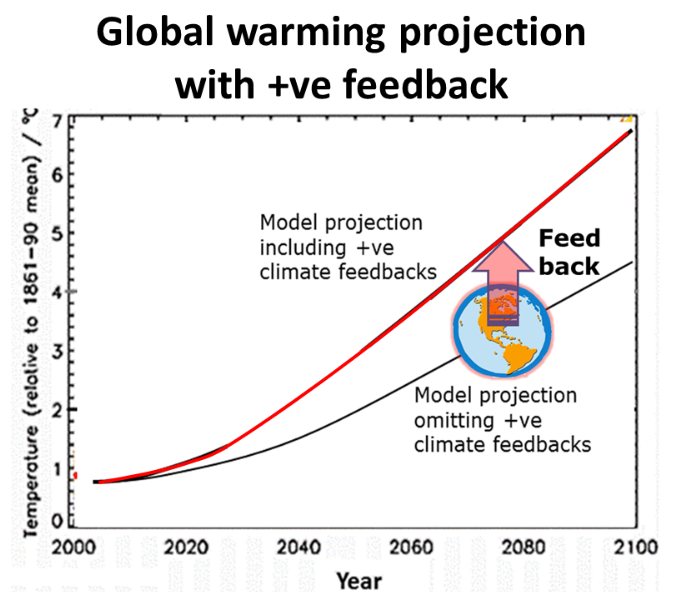
In the case of global climate change positive feedbacks to global warming lead to more global warming. Global warming causes more global warming
Furthermore the increased warming accelerates over time and temperature.
Climate system +ve feedback is a global warming impact multiplier.
Considering all the feedbacks the +ve feedbacks are incomparably larger the -ve, and
the more the warming the larger the +ve feedbacks (but not the -ve).
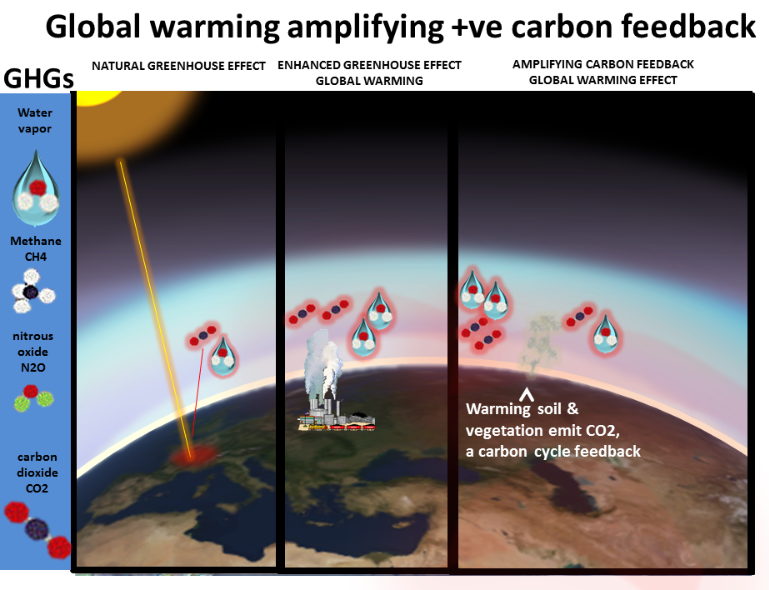
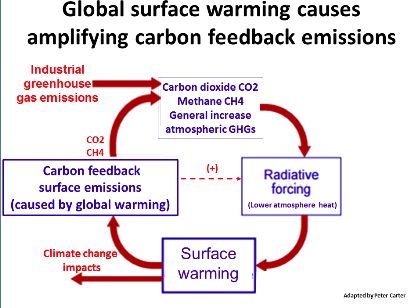
Positive feedbacks that operate by the planet emitting more carbon dioxide (CO2) or methane (CH4) are +ve carbon (cycle) feedbacks.
By definition positive carbon feedback is the greatest risk caused by global warming - because our industrial global warming responds by emitting carbon GHGs CO2 and methane and that boosts global warming more that increases carbon feed back even more etc... - in the ultimate vicious cycle.
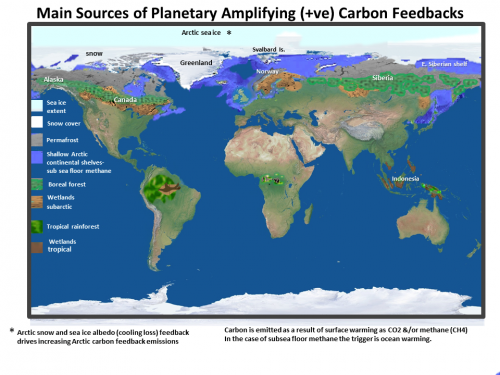
There are a great many of the +ve feedbacks and Earth has vast pools (stores) of carbon vulnerable to global warming- the largest being Arctic.
The warming planet emits CO2 methane and nitrous oxide- thawing permafrost is doing all this now.
Climate system positive feedbacks or loops tend to be self perpetuating and accelerating making them catastrophically dangerous.
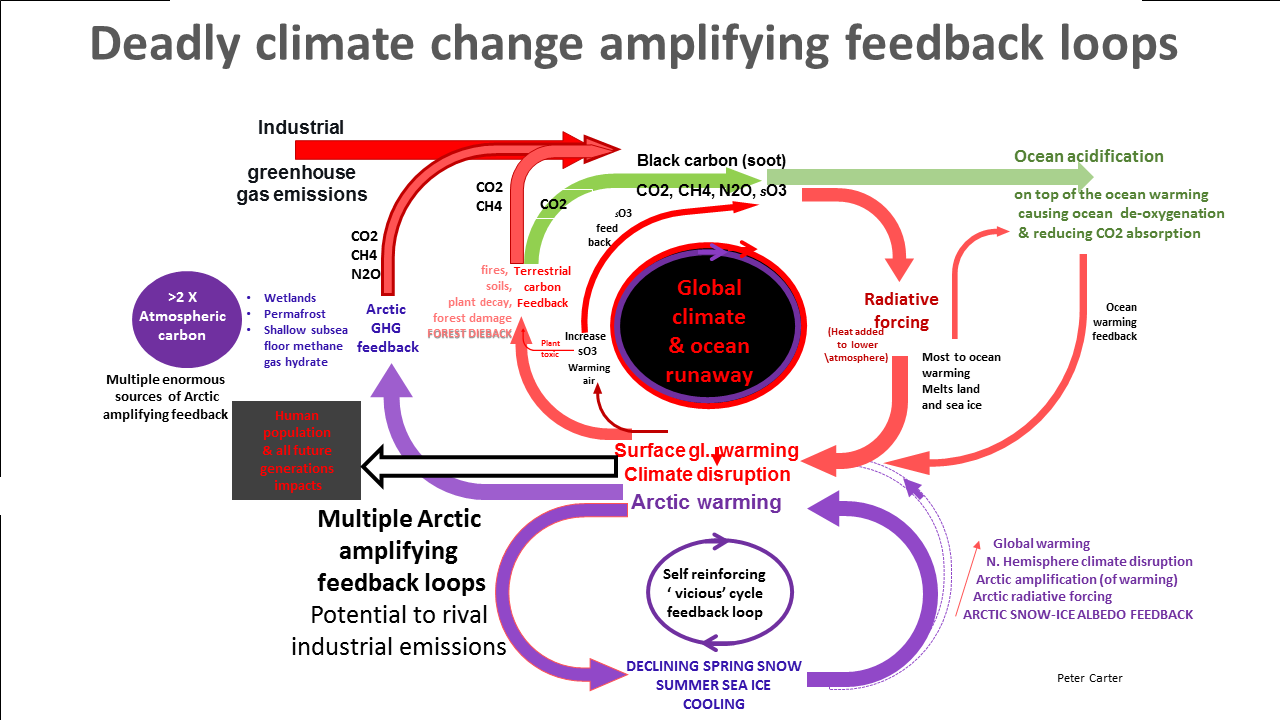
One positive feedback may increase one or more other positive feedbacks - 'cascading' feedbacks, which leads to runaway rapid warming.
The big example is the Arctic involving Arctic methane.
There are unforeseen positive feedbacks
The melting of glaciers forms deep channels of water torrents and lake at
the glacier base lubricating its retreat.
Fast and Slow feedbacks
There are 2 sorts of feedbacks in terms of their speed of response.
Fast feedbacks (or Charney feedbacks) are the only ones accounted for
by the IPPC in global warming projections are the fast feedbacks.
These act on an immediate time scale and are water vapor, clouds
(+ve & -ve) aerosols (+ve and -ve). latest research confirms the strong
water vapor feedback and that clouds have a net positive (bad) feedback
Water vapor is a GHG and the largest +ve feedback.
It about doubles the warming caused by a GHG alone.
Warm air holds more water as global warming increases so amplifying
the global warming by a factor of 2 for warming by GHG alone.
It is a fast feedback
Slow feedbacks are much slower to respond to warming, but as they do
they are very large and can lead to catastrophic accelerating degrees of
warming.
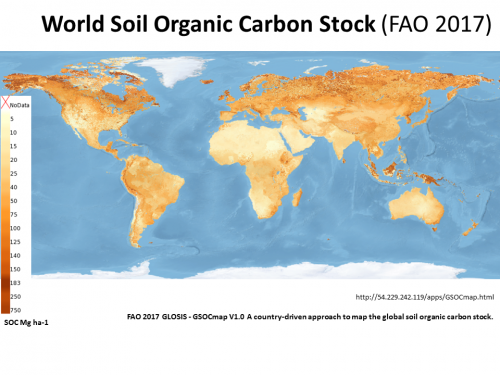
They are the albedo cooling loss from the loss of ice sheets, warming wetland
peat (high carbon), thawing permafrost (CO2 CH4 N2O) and sub sea floor methane.
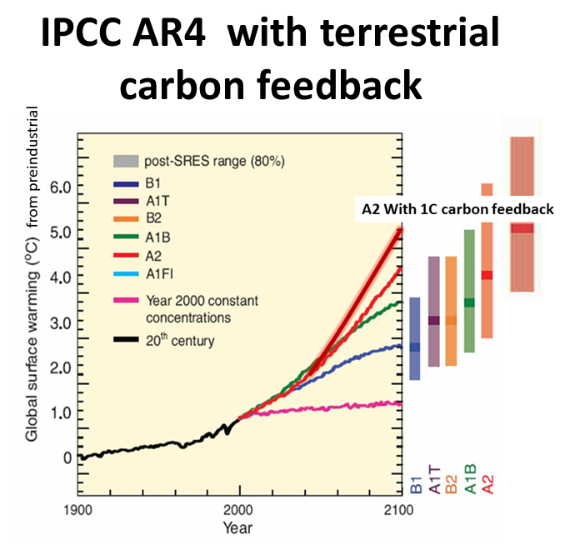
These large slow feedback are excluded by the IPCC global warming projections
in the assessments. They are also not included in the calculation of the all
important climate sensitivity.
There are two kinds of feedback in terms of amplifying warming (+ve) or reducing warming (-ve).
We are most used to negative feedback systems used for safety. If a heater gets to hot there is a built -ve feedback that switches it off.
But in the climate system there is no such safety mechanism- feedbacks act in the dangerously +ve feedback way.
In the case of global climate change positive feedbacks to global warming lead to more global warming. Global warming causes more global warming
Furthermore the increased warming accelerates over time and temperature.
Climate system +ve feedback is a global warming impact multiplier.
Considering all the feedbacks the +ve feedbacks are incomparably larger the -ve, and
the more the warming the larger the +ve feedbacks (but not the -ve).
Positive feedbacks that operate by the planet emitting more carbon dioxide (CO2) or methane (CH4) are +ve carbon (cycle) feedbacks.
By definition positive carbon feedback is the greatest risk caused by global warming - because our industrial global warming responds by emitting carbon GHGs CO2 and methane and that boosts global warming more that increases carbon feed back even more etc... - in the ultimate vicious cycle.
There are a great many of the +ve feedbacks and Earth has vast pools (stores) of carbon vulnerable to global warming- the largest being Arctic.
The warming planet emits CO2 methane and nitrous oxide- thawing permafrost is doing all this now.
Climate system positive feedbacks or loops tend to be self perpetuating and accelerating making them catastrophically dangerous.
One positive feedback may increase one or more other positive feedbacks - 'cascading' feedbacks, which leads to runaway rapid warming.
The big example is the Arctic involving Arctic methane.
There are unforeseen positive feedbacks
The melting of glaciers forms deep channels of water torrents and lake at
the glacier base lubricating its retreat.
Fast and Slow feedbacks
There are 2 sorts of feedbacks in terms of their speed of response.
Fast feedbacks (or Charney feedbacks) are the only ones accounted for
by the IPPC in global warming projections are the fast feedbacks.
These act on an immediate time scale and are water vapor, clouds
(+ve & -ve) aerosols (+ve and -ve). latest research confirms the strong
water vapor feedback and that clouds have a net positive (bad) feedback
Water vapor is a GHG and the largest +ve feedback.
It about doubles the warming caused by a GHG alone.
Warm air holds more water as global warming increases so amplifying
the global warming by a factor of 2 for warming by GHG alone.
It is a fast feedback
Slow feedbacks are much slower to respond to warming, but as they do
they are very large and can lead to catastrophic accelerating degrees of
warming.
They are the albedo cooling loss from the loss of ice sheets, warming wetland
peat (high carbon), thawing permafrost (CO2 CH4 N2O) and sub sea floor methane.
These large slow feedback are excluded by the IPCC global warming projections
in the assessments. They are also not included in the calculation of the all
important climate sensitivity.
CLIMATE EMERGENCY INSTITUTE

Ice cores show that warm interglacial periods are from feed-back emissions triggered by a tiny increase in insolence Causal feedbacks in climate change
The Arctic has switched from carbon sink to source with accelerating Arctic permafrost feedback underway(NOAA 2019 Arctic Report Card)

Amazon is carbon source confirmed ( 2021)
2021 VIDEOs Climate Emergency Feedback
Surface Ozone: major ignored feedback
Atmospheric methane's explosive increase from wetland feedback emissions
20 March 2023, Recent intensification of wetland methane feedback, Zhen Zhang et al From Tropical wetlands (largest S. America) High-latitude wetlands appear to have only moderate CH4 increases
20 March 2023, Recent intensification of wetland methane feedback, Zhen Zhang et al From Tropical wetlands (largest S. America) High-latitude wetlands appear to have only moderate CH4 increases
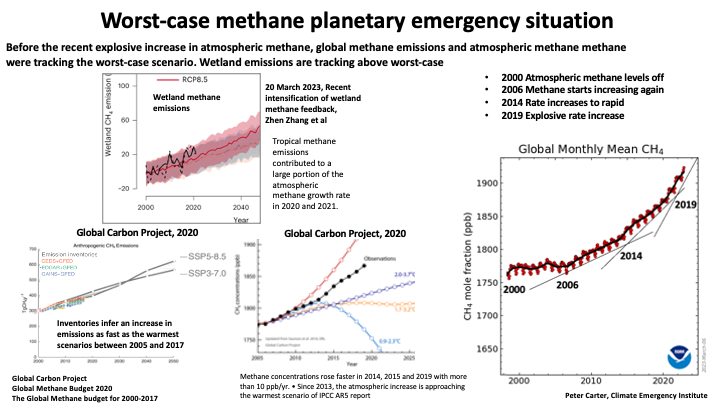
We determine that wetlands will form the majority of the CH4 climate feedback up to 2100 March 2018 Methane Feedbacks to the Global Climate System in a Warmer World, J.F. Dean et al
+ve means amplifying (bad)
Double click here to edit this text.