Temperature Increase
Global warming Global warming is defined in this report as an increase in combined surface air and sea surface temperatures averaged over the globe and over a 30-year period expressed relative to the period 1850–1900, as pre-industrial temperatures (IPCC) The 20th century average often used as baseline is 1901-2000
Climate Emergency Institute
Global warming is higher :
>in the night-time than the day (March 10, 2016,
>in the night-time than the day (March 10, 2016,
>over land than over sea
(sea surface temperature SST )
>over central continents
>in the northern hemisphere than southern and
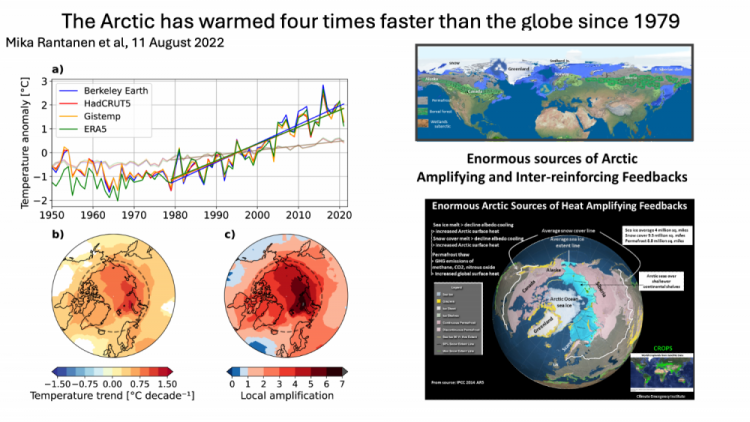
> highest in the Arctic
(feedback amplification)
(sea surface temperature SST )
>over central continents
>in the northern hemisphere than southern and
> highest in the Arctic
(feedback amplification)
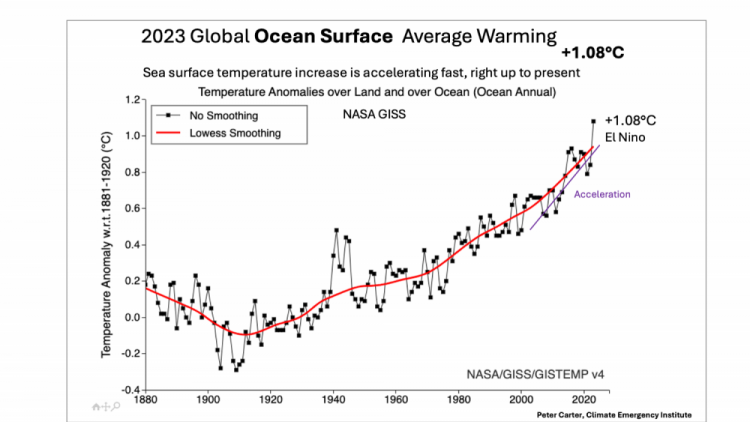
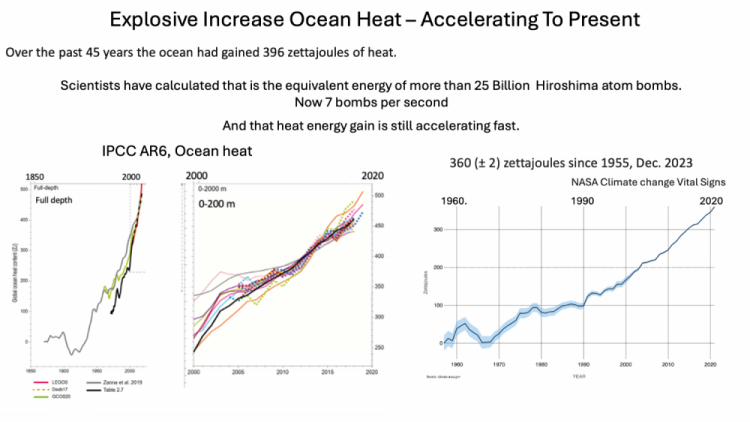
OCEANS Record high ocean heat is increasing at accelerating rate.
93% of added GHG heat has gone to the oceans, making ocean heat a much better single guide for assessment and mitigation than global surface warming. Global warming varies,with volcanic eruptions, El Nino La Nina phases, while ocean heat does not.
93% of added GHG heat has gone to the oceans, making ocean heat a much better single guide for assessment and mitigation than global surface warming. Global warming varies,with volcanic eruptions, El Nino La Nina phases, while ocean heat does not.

Baselines
20th century average is 1901-2000
Pre-industrial correction is 0.24°C
Copernicus 1991-2020 add 0.87°C
20th century average is 1901-2000
Pre-industrial correction is 0.24°C
Copernicus 1991-2020 add 0.87°C
Aspects of global warming
Global warming is average Land-ocean, the ocean having a cooling effect.
Global warming is the annual average.
Global warming average has been taken as a 30-year average, but WMO says a 10-yr average can be acceptable.
El Nino/La Nina
Global tends to be higher in an El Nino phase and cooler in La Nina
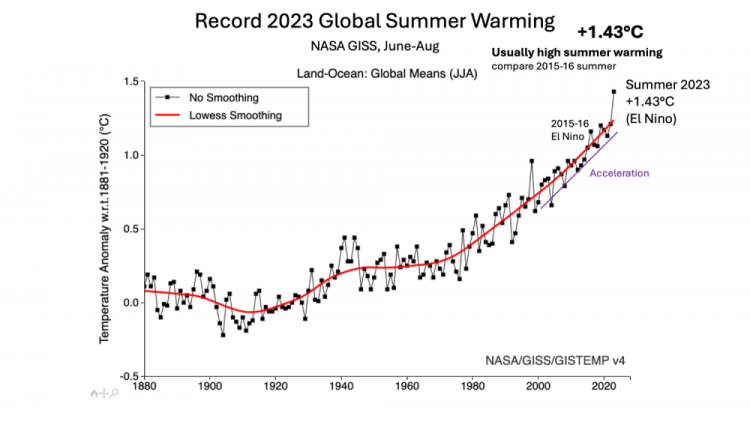
Global summer warming would be more useful, for heat waves, wild-fires, drought
Global warming is average Land-ocean, the ocean having a cooling effect.
Global warming is the annual average.
Global warming average has been taken as a 30-year average, but WMO says a 10-yr average can be acceptable.
El Nino/La Nina
Global tends to be higher in an El Nino phase and cooler in La Nina
Global summer warming would be more useful, for heat waves, wild-fires, drought
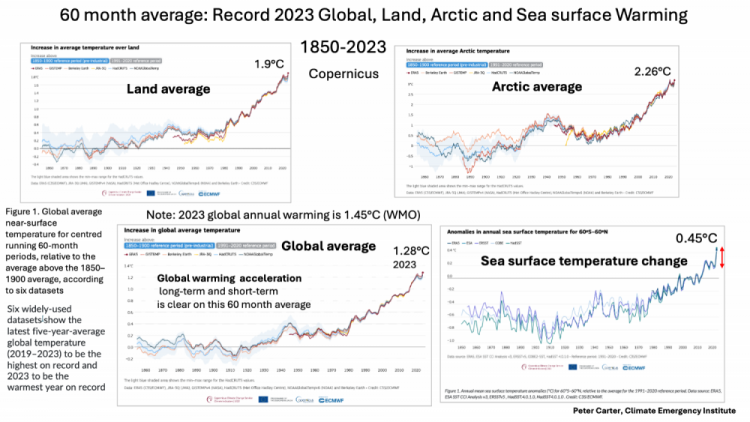
60 month average to 2023
from Copernicus
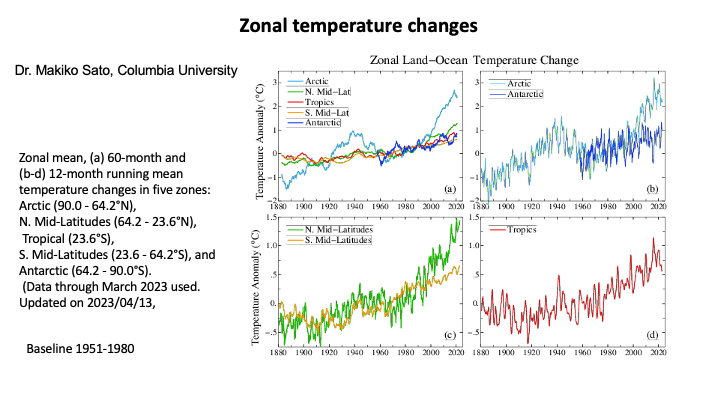
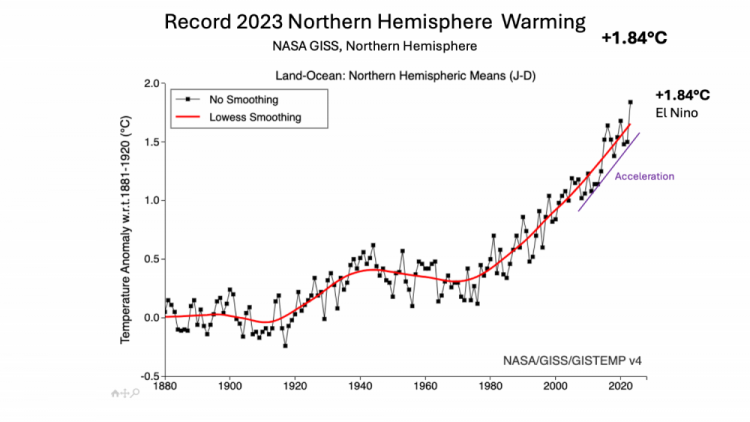
Northern hemisphere warming is much faster than the global average
Arctic is fastest of all
up to 4X global average.
Sea surface is slowest cooling the global average.
from Copernicus
Northern hemisphere warming is much faster than the global average
Arctic is fastest of all
up to 4X global average.
Sea surface is slowest cooling the global average.
Causes for the big record 2023 warming
1. Record atmospheric CO2, increasing faster than ever
2. Record all atmospheric GHGs
3. El Nino
4. Decline of cooling aerosol emissions -
measures have been taken to further reduce fossil fuel
air pollution reducing air pollution sulfate cooling aerosols
1. Record atmospheric CO2, increasing faster than ever
2. Record all atmospheric GHGs
3. El Nino
4. Decline of cooling aerosol emissions -
measures have been taken to further reduce fossil fuel
air pollution reducing air pollution sulfate cooling aerosols
8th June 2023, Indicators of Global Climate Change 2022, M. Forster et al
Over the 2013–2022 period,human-induced warming has been increasing at an unprecedented rate of over 0.2°C per decade. This high rate of warming is caused by a combination of greenhouse gas emissions being at an all-time high over the last decade, as well as reductions in the strength of aerosol cooling.
Over the 2013–2022 period,human-induced warming has been increasing at an unprecedented rate of over 0.2°C per decade. This high rate of warming is caused by a combination of greenhouse gas emissions being at an all-time high over the last decade, as well as reductions in the strength of aerosol cooling.
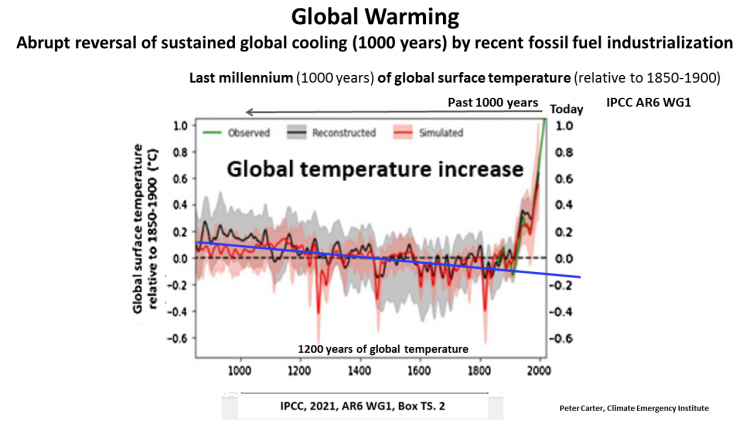
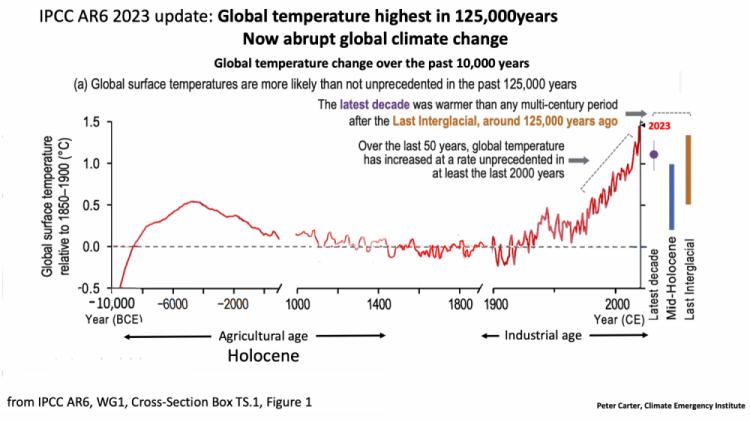
Global warming past 1000 years
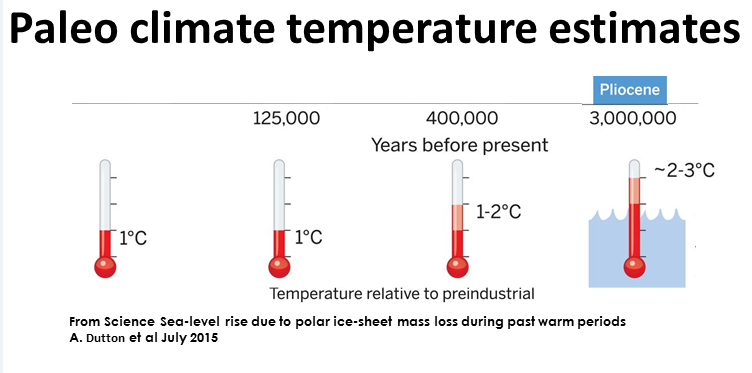
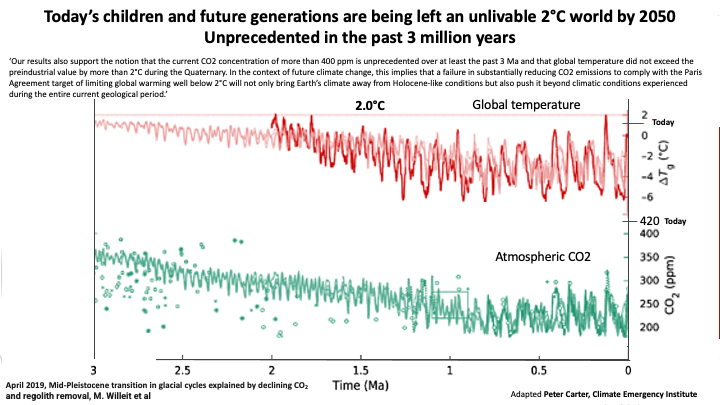
2023 temperature highest
in 125,000 years
in 125,000 years
Arctic temperature
The Arctic is now heating at twice the global rate as the science has said for years- From 1980 to 2021 its heated up to 4x as fast as the rest of the planet. That puts the Arctic amplifying feedbacks and tipping points coming on much faster.
The Arctic holds more carbon, till recently safely frozen, than other region on the planet. Yes - another reason for immediate global emissions decline.
The Arctic is now heating at twice the global rate as the science has said for years- From 1980 to 2021 its heated up to 4x as fast as the rest of the planet. That puts the Arctic amplifying feedbacks and tipping points coming on much faster.
The Arctic holds more carbon, till recently safely frozen, than other region on the planet. Yes - another reason for immediate global emissions decline.
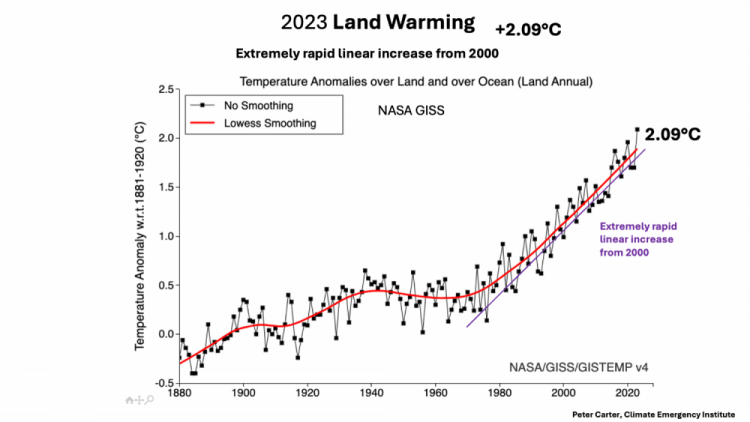
Land (only) warming 2023
Sea surface warming 2023
Summer warming 2023
Northern hemisphere 2023 +1.84°C
We need to know warming in the summer
for heat waves, wild fires and drought
for heat waves, wild fires and drought

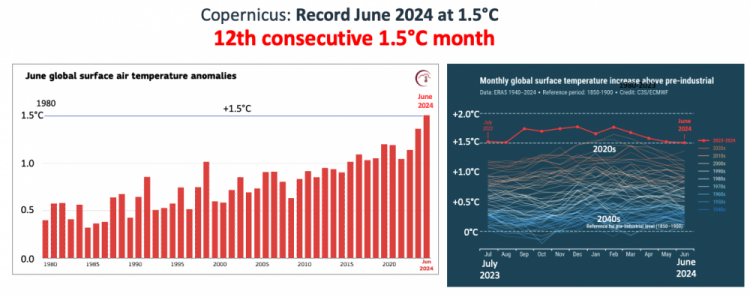
Juine 2024 Record of records
June record at +1.5°C
13 record consecutive months
12 months above/at +1.5°C
(Copernicus)
13 record consecutive months
12 months above/at +1.5°C
(Copernicus)
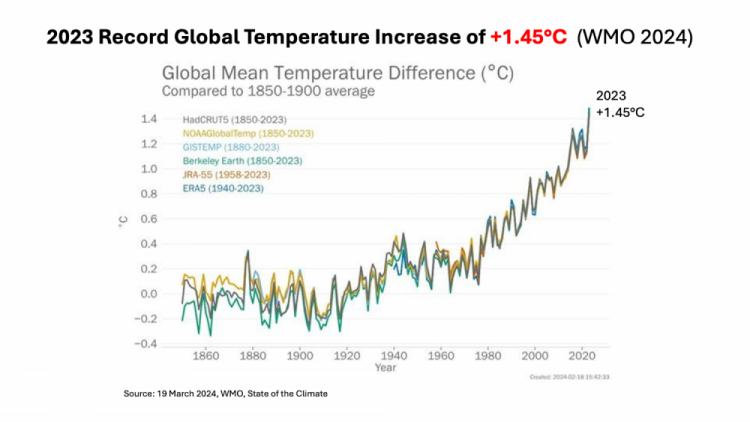
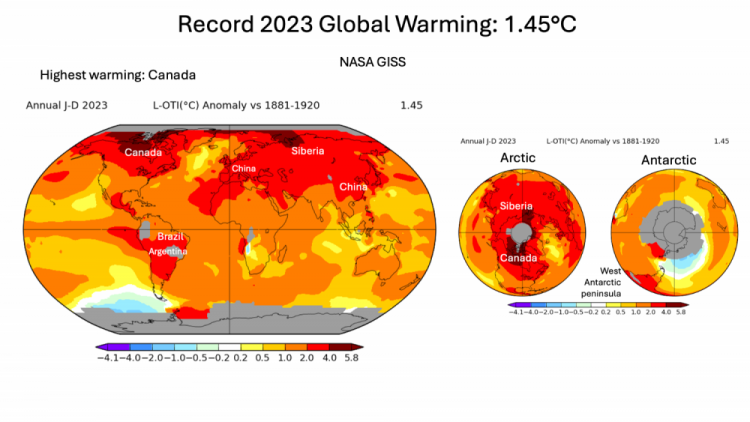
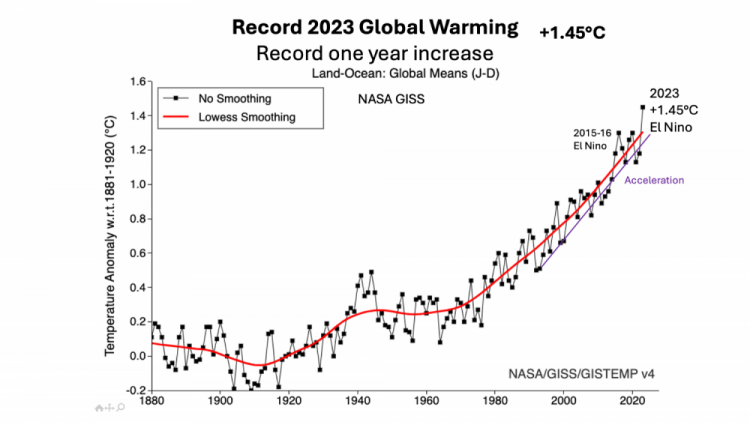
Big Record 2023 +1.45°C
2023 global warming was a record by a record large margin,
boosted by a powerful El Nino
WMO put it at 1.45°C
(climate centers varies slightly)
It was the highest global temperature
in 125,000 years
(climate centers varies slightly)
It was the highest global temperature
in 125,000 years
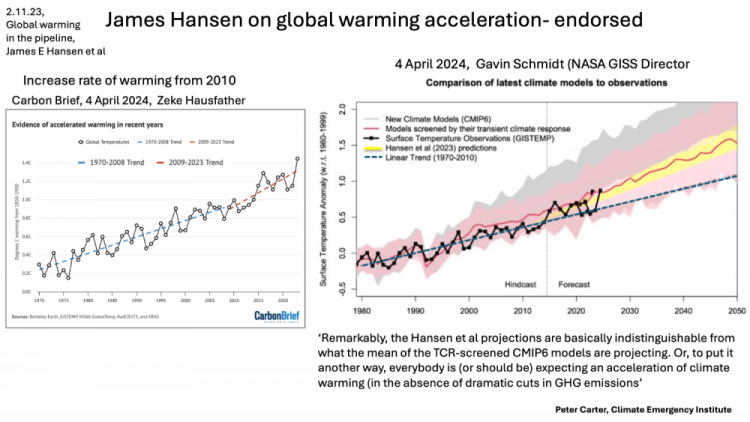
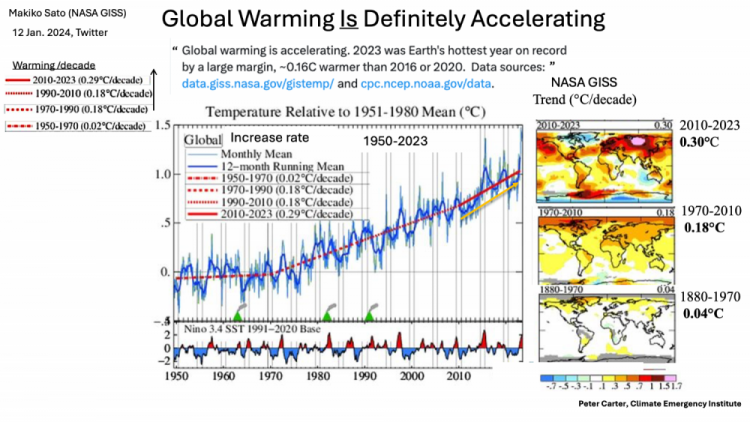
Global warming is accelerating
even without big 2023 record
even without big 2023 record
Global warming long term trend is acceleration
Recent global warming is accelerating
(James Hansen confirmed by Gavin Schmidt
Global warming Acceleration
Dr. Makiko Sato (NASA) Jan. 2024
Industrial global warming is extremely rapid
an abrupt global temperature increase
an abrupt global temperature increase
More on the 2023 record
Clear acceleration
Long & short terms
Long & short terms
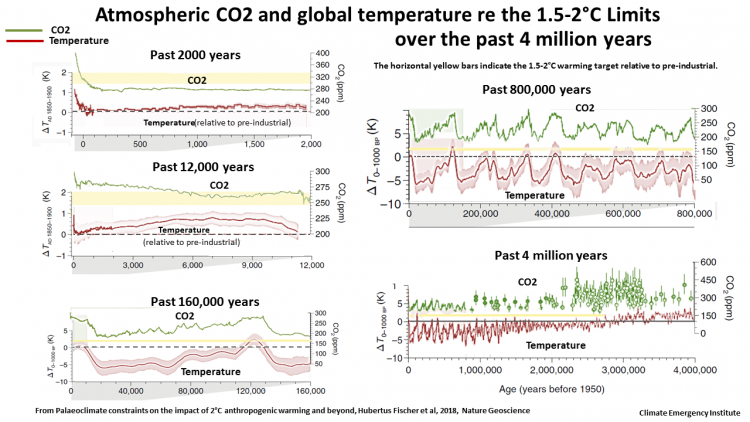
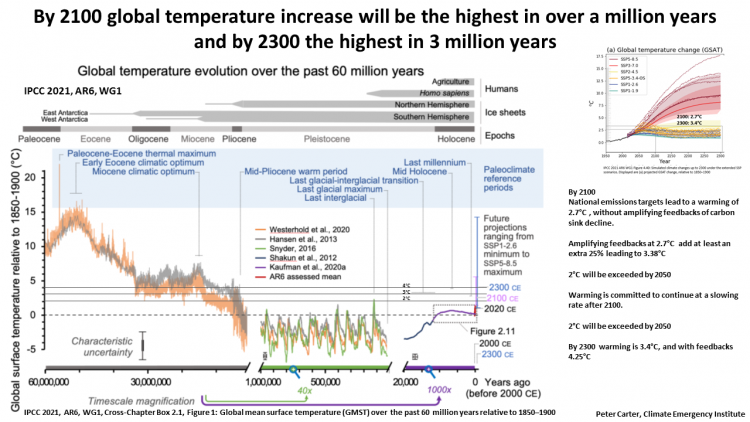
Global temperatures in the distant past
Global temperature is now very high with respect to past million of years
Global temperature is now very high with respect to past million of years
Marine heat waves
Ocean marine heat waves are increasing
2023 was a record for marine heat waves
On an average day in 2023, nearly one third of the global ocean was gripped by a marine heatwave, harming vital ecosystems and food systems. Towards the end of 2023, over 90% of the ocean had experienced heatwave conditions at some point during the year (WMO March 2024, State of Climate in 2023).
Ocean marine heat waves are increasing
2023 was a record for marine heat waves
On an average day in 2023, nearly one third of the global ocean was gripped by a marine heatwave, harming vital ecosystems and food systems. Towards the end of 2023, over 90% of the ocean had experienced heatwave conditions at some point during the year (WMO March 2024, State of Climate in 2023).
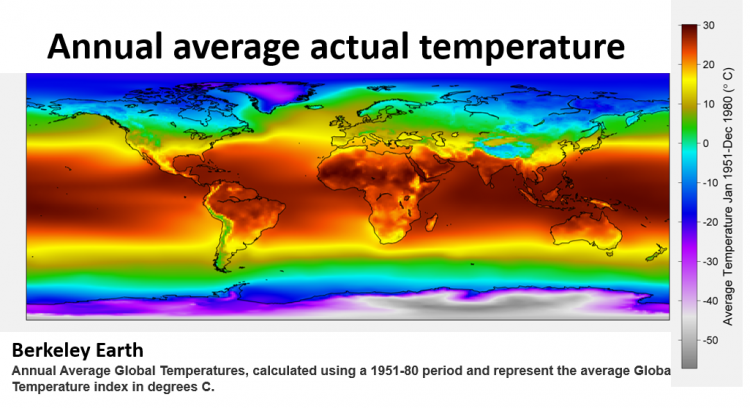
1900, average global temperature:
13.7° Celsius
13.7° Celsius